Feature Update: Detect Variants That Disrupt Splicing
Genetic variations impact gene translation beyond simple amino acid substitutions. A single nucleotide change or indel can disrupt a splice site, altering the final polypeptide product of a gene. Our “Translation Changes” interface highlights variants that lead to modified protein sequences. In the latest update, Persephone now also flags alleles that affect splicing sites or disrupt start and stop codons, providing deeper insights into translation changes. We assume that changing the nucleotides at the donor or acceptor sites leads to intron retention, so we continue translating into the nucleotide regions normally spliced out. Including intron sequences into a CDS typically leads to frame shifts and premature translation termination.
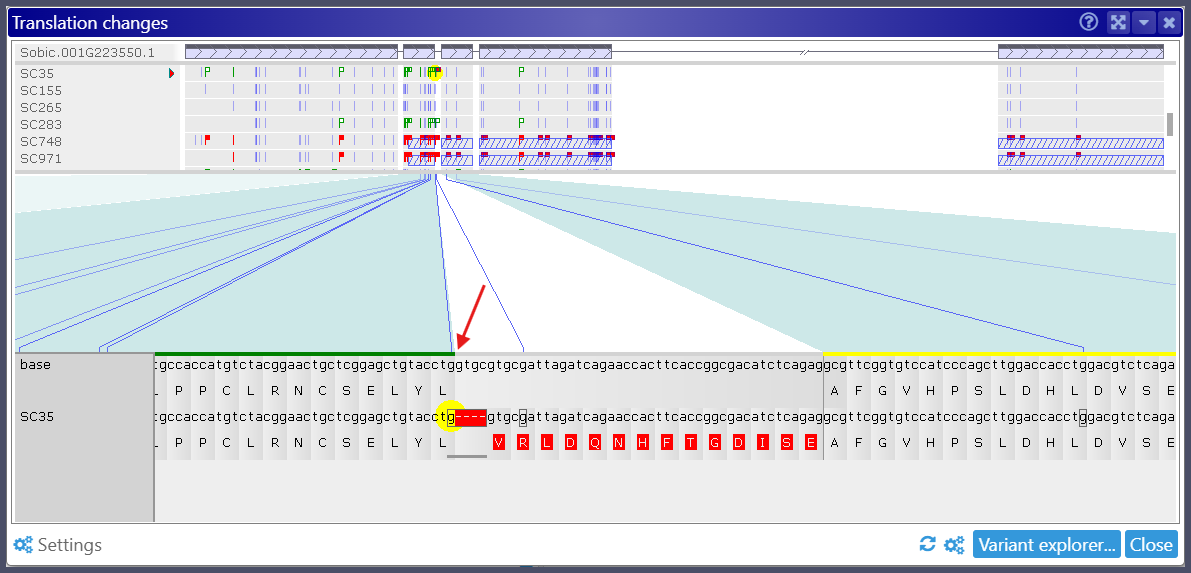
The visualization of premature stop codons resulting from the variation is improved by highlighting the segment of the CDS that will be excluded from translation. This omitted portion will be represented with a striped pattern.



